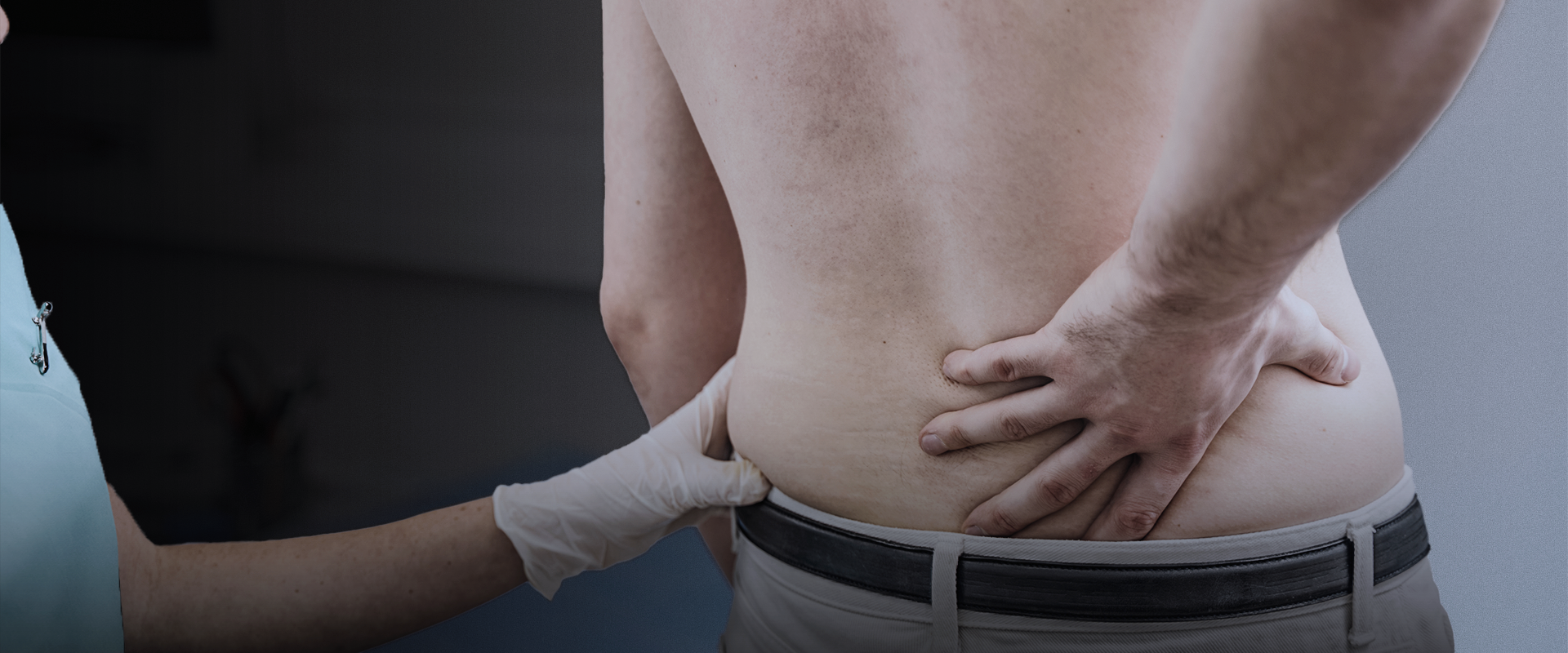
Physical Therapy for back strain
AT EVOLVE
Physical Therapy for a back strain
HOW CAN PHYSICAL THERAPY ADDRESS BACK STRAINS?
A back strain is an injury to the muscles or tendons along the upper, middle or lower back. A back sprain describes an injury to one or more of the ligaments along the spine. While these names sound similar, they are used to describe injuries to different structures. Back strains often occur during exercise or training but can occur unexpectedly during an accident or simple daily task. Physical therapists are healthcare professionals trained to assess and treat musculoskeletal injuries like back strains. Physical therapy can reduce pain and stiffness, improve strength, flexibility and stability in the back and help you resume sports and activities of daily living.
WHAT DOES PHYSICAL THERAPY FOR A BACK MUSCLE STRAIN LOOK LIKE?
Physical therapy for a back strain aims to reduce pain and stiffness, restore normal strength and range of motion and facilitate return to full activities. My team of therapists and I will start by getting to know your concerns and goals and performing a thorough physical exam to determine what areas we should target with our physical therapy interventions. Your therapist will employ manual therapy interventions to target joint and tissue mobility while also prescribing movements and exercises for strength, flexibility, motor control and mobility to be performed in the home and the clinic. Modalities to control pain and inflammation and promote healing may also be utilized. We will guide you through each step of the rehabilitation process from the onset of injury to your return to full activity.
HOW LONG WILL I NEED PHYSICAL THERAPY?
The duration of your physical therapy plan of care for a back strain will vary depending on the severity of the strain and your symptoms, as well as the types of activities you aim to resume. Individuals such as weight lifters, athletes, manual laborers or even parents who lift and carry their children may require a longer course of care than those who do not use their backs in such a way. While full resolution of symptoms can take some time, you may see some results quickly. You should experience improvements in many symptoms such as pain, stiffness, and inflammation within a couple of weeks but returns in strength, flexibility and overall activity tolerance may take longer. Achieving long-lasting results may take some time, but dedication to your program will not only help you achieve these results but will help to decrease the likelihood of symptoms recurring in the future.
ANATOMY OF A BACK MUSCLE STRAIN
When a muscle is overstretched, asked to contract hard against a sudden load, or overused, injury can occur. Small tears in the muscle fibers or the fibers of the tendon that connect the muscle belly to nearby bone are called muscle strains. A back strain involves one of the many muscles and tendons positioned along the back. We can categorize back muscles based on function:
- Deep muscles that help control the spine
- Superficial muscles that help move the spine
- Superficial muscles that move the scapula and shoulder girdle
A back strain can occur in several ways:
- Overuse–Example: a dad who lifts his child repeatedly or a landscaper working long hours to finish a job
- Sudden high load–Example: lifting a weight that is too heavy at the gym
- Overstretch–Example: suddenly twisting during a fall or hyperflexion of the spine
WHAT DOES A BACK STRAIN FEEL LIKE?
When a muscle or tendon is strained, you will experience pain in that specific muscle or tendon when it is contracted strongly or stretched. Because many back muscles overlap, it can be difficult to tell exactly which muscle is injured. An examination by a doctor or physical therapist can usually identify the muscle based on the motions that provoke symptoms. If the strain is moderate in severity, you may also notice some localized stiffness, tenderness, and swelling. You may also observe that the muscle feels weaker than usual. If the strain is severe, the muscle belly can tear completely or separate from the tendon causing the range of motion in the joints at either end of the muscle to be either significantly reduced because of guarding or excessive because the torn muscle or tendon is no longer limiting it.
It is important to note that when a muscle or tendon has been severely torn, your doctor may recommend surgery to repair the injury so the muscle can function normally again. After surgery, or when it is not needed, physical therapy is just what the doctor ordered.
End Injury Progression
Physical Therapy for a back strain has proven to prevent injury, slow and even stop pain issues, improve performance, and reverse injury progression in many cases.
Relieve Pain
The movements used in this technique can target your entire body helping you to manage discomfort and pain during the course of your physical therapy treatments.
Improve Range of Motion
Posture awareness is an important area to focus on due to the fact that certain positions may cause you further discomfort and pain.
Restore Mobility
You can regain mobility and flexibility by taking part in the stretches and exercises as prescribed by your physical therapist.
How Long Will Physical Therapy for back strain Last?
If you decide to work with a physical therapist to help correct your back strain issues, your entire treatment plan could consist of around 8-20+ different physical therapy sessions that will each last 60-90 minutes. Once you complete your customized physical therapy treatment plan, you will be able to continue to do the prescribed stretches and exercises utilized during your back strain PT sessions yet in the comfort of your own home.
PHYSICAL THERAPISTS CAN HELP YOU RECOVER
While mild back strains often recover on their own within a couple of weeks, you may choose to see a physical therapist to address a more severe strain or if the symptoms of a mild strain are interfering with your activities. The goals and interventions for rehabilitation of a back muscle strain can be broken down into three stages:
Early/acute phase (first 5-7 days):
- Protect the injured muscle or tendon to allow healing to begin
- Use bracing and taping as needed to minimize painful motions
- Consider ice, ultrasound or other modalities to manage inflammation and promote healing
- Range of motion that is pain-free may be used to prevent stiffness, maintain range of motion and reduce pain
- Low-grade joint mobilizations for pain may be administered
- Exercising nearby but uninjured areas of the body is helpful
Middle/subacute phase (7-21 days or so after injury)
- Advance active range of motion
- Wean off bracing, taping, etc
- Begin submaximal exercise to lightly load the muscle and promote good fiber alignment
- Begin very light stretching as needed
- Apply gentle soft tissue mobilization to promote healing, reduce pain and mobilize edema
Late/chronic phase (21 days to many months)
- Begin loading the muscle more intensively while monitoring for signs of acute regression including lasting soreness or inflammation
- Increase the load on resistance training
- Increase stretching and mobility
- Begin exercises to improve tendon stiffness
- Incorporate more dynamic spinal exercises
- Perform work and sport-specific drills to prepare the back to return to full activity
DON’T GO IT ALONE
As you can see, recovering well from a back strain requires knowledge of the healing process. Whether you are experiencing a back strain for the first time or are stuck in a cycle of healing and re-injury, physical therapy is a fantastic resource to help you recover. There is no need to go it alone. The physical therapists at Evolve are here to educate you on the healing process, get you back to your favorite activities and teach you how to prevent re-injury. Call today to schedule an initial evaluation. Call to Schedule a Consultation! 1-718-258-3300
Marine Park
3319 Avenue N
Brooklyn, NY 11234
Monday-Thursday: 8am-8pm
Friday: 8am-3pm
Mill Basin (located in Harbor Fitness)
6161 Strickland Ave
Brooklyn, NY 11234
Monday: 7am-8pm
Tuesday: 7am-8pm
Wednesday: 8am-5pm
Thursday: 7am-8pm
Friday: 8am-1pm
Park Slope (located in Harbor Fitness)
550 5th Ave.
Brooklyn, NY 11215
Monday: 9am-8pm
Tuesday: 8am-6pm
Wednesday: 9am-8pm
Thursday: 8am-6pm
Friday: 8am-3pm
Gravesend
372 Avenue U
Brooklyn, NY 11223
Monday-Thursday: 8am-8pm
Friday: 8am-3pm
Kings Highway
945 Kings Highway
Brooklyn, NY 11223
Monday-Wed.: 12pm-8pm
Ready to take the next step to a healthier you?
Contact Us Today!
PHYSICAL THERAPY FOR BACK STRAIN
Need physical therapy for a strained back?
Let our caring and compassionate physical therapists help you with relieving pain while getting you back on your feet comfortably.
Call now to schedule your first PT consultation free of charge.
Call: 1-718-751-0741